Computed Tomography
What is a CT Scan?
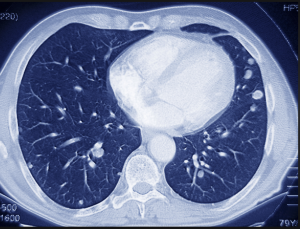 CT (computed tomography), sometimes called CAT scan, uses special x-ray equipment to obtain image data from different angles around the body and then uses computer processing of the information to show a cross-section of body tissues and organs.
CT (computed tomography), sometimes called CAT scan, uses special x-ray equipment to obtain image data from different angles around the body and then uses computer processing of the information to show a cross-section of body tissues and organs.
CT imaging is particularly useful because it can show several types of tissue — lung, bone, soft tissue and blood vessels—with great clarity. Using specialized equipment and expertise to create and interpret CT scans of the body, radiologists can more easily diagnose problems such as cancers, cardiovascular disease, infectious disease, trauma and musculoskeletal disorders.
Lakes Radiology has the latest technology in (MDCT) CT scanning, this revolutionary system is emerging as a highly effective screening tool in the early detection of heart disease and other serious medical conditions — even years before major symptoms occur.
Our GE LightSpeed Plus High Speed Multislice CT Scanner allows very fast scanning.. so fast in fact that most scans can be performed in less than a minute. these subsecond scans result in much improved quality because of decresased patient motion and fast adquisitions, as usual we have choosen a patient friendly scanning of all patients, large, small and claustrophobic or not.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
Because it provides detailed, cross-sectional views of all types of tissue, CT is one of the best tools for studying the chest and abdomen. It is often the preferred method for diagnosing many different cancers, including lung, liver and pancreatic cancer, since the image allows a physician to confirm the presence of a tumor and measure its size, precise location and the extent of the tumor’s involvement with other nearby tissue.
CT examinations are often used to plan and properly administer radiation treatments for tumors, to guide biopsies and other minimally invasive procedures and to plan surgery and determine surgical resectability. CT can clearly show even very small bones as well as surrounding tissues such as muscle and blood vessels. This makes it invaluable in diagnosing and treating spinal problems and injuries to the hands, feet and other skeletal structures. CT images can also be used to measure bone mineral density for the detection of osteoporosis.
In cases of trauma, CT can quickly identify injuries to the liver, spleen, kidneys or other internal organs. Many dedicated shock-trauma centers have a CT scanner in the emergency room. CT can also play a significant role in the detection, diagnosis and treatment of vascular diseases that can lead to stroke, kidney failure or even death.
How should I prepare for the CAT scan?
You should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing for your CT exam. Metal objects can affect the image, so avoid clothing with zippers and snaps. You may also be asked to remove hairpins, jewelry, eyeglasses, hearing aids and any removable dental work, depending on the part of the body that is being scanned. You may be asked not to eat or drink anything for one or more hours before the exam. Women should always inform their doctor or x-ray technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant.
How is the CAT scan performed?
 The technologist begins by positioning the patient on the CT table. The patient’s body may be supported by pillows to help hold it still and in the proper position during the scan. As the study proceeds, the table will move slowly into the CT scanner. Depending on the area of the body being examined, the increments of movement may be so small that they are almost undetectable or large enough that the patient feels the sensation of motion.
The technologist begins by positioning the patient on the CT table. The patient’s body may be supported by pillows to help hold it still and in the proper position during the scan. As the study proceeds, the table will move slowly into the CT scanner. Depending on the area of the body being examined, the increments of movement may be so small that they are almost undetectable or large enough that the patient feels the sensation of motion.
A CT examination often requires the use of different contrast materials to enhance the visibility of certain tissues or blood vessels. The contrast material may be swallowed, injected through an IV directly into the blood stream or administered by enema, depending on the type of examination. Before administering the contrast material, the radiologist or technologist may ask whether the patient has any allergies, especially to medications or iodine, and whether the patient has a history of diabetes, asthma, a heart condition, kidney problems or thyroid conditions. These conditions may indicate a higher risk of reaction to the contrast material or potential problems eliminating the material from the patient’s system after the exam.
A CT examination usually takes five minutes to half an hour. When the exam is over the patient may be asked to wait until the images are examined to determine if more images are needed.
Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
A radiologist, who is a physician experienced in CT and other radiology examinations, will analyze the images and send a signed report with his or her interpretation to the patient’s personal physician. The personal physician’s office will inform the patient on how to obtain their results. New technology also allows us the distribution of diagnostic reports and referral images over the Internet.
ACR Accreditation
 Lakes Radiology is an accredited facility with the American College of Radiology to perform the low dose lung CT, the only recommended screening test for lung cancer. This test is a low-dose computed tomography exam (also called a low-dose CT scan, or LDCT).
Lakes Radiology is an accredited facility with the American College of Radiology to perform the low dose lung CT, the only recommended screening test for lung cancer. This test is a low-dose computed tomography exam (also called a low-dose CT scan, or LDCT).
The American College of Radiology® (ACR®) is a nonprofit professional society representing radiologists, nuclear medicine physicians, radiation oncologists and medical physicists. It is the largest and oldest imaging accrediting body in the U.S., with a current membership of 39,000 physicians and medical physicists. The core purpose of the ACR is to serve patients and society by empowering its members to advance the practice, science and professions of radiological and radiation oncology care.
Schedule an appointment
To schedule an appointment at Lakes Radiology please call (305) 231-1115 or fill out the form below.
Our Services
Business Hours
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Saturday
- Sunday
- 8AM - 5PM
- 8AM - 5PM
- 8AM - 5PM
- 8AM - 5PM
- 8AM - 5PM
- 8AM - 3PM
- Closed
